What Tests Does a Durable Data Cable Go Through?

2026-01-29 13:34

Frayed jackets, exposed wires, or complete cable failure are common frustrations for users.
But before a data cable ever reaches a retail shelf, it must survive a series of industrial-level reliability tests on the production line.
So what physical limits must a qualified data cable pass before it can be shipped?
In this article, BWOO walks you through the industry-recognized reliability tests used across the mobile accessories sector, and explains how durability is defined by international standards rather than marketing claims.
The Four Core Physical Challenges Recognized by the Industry
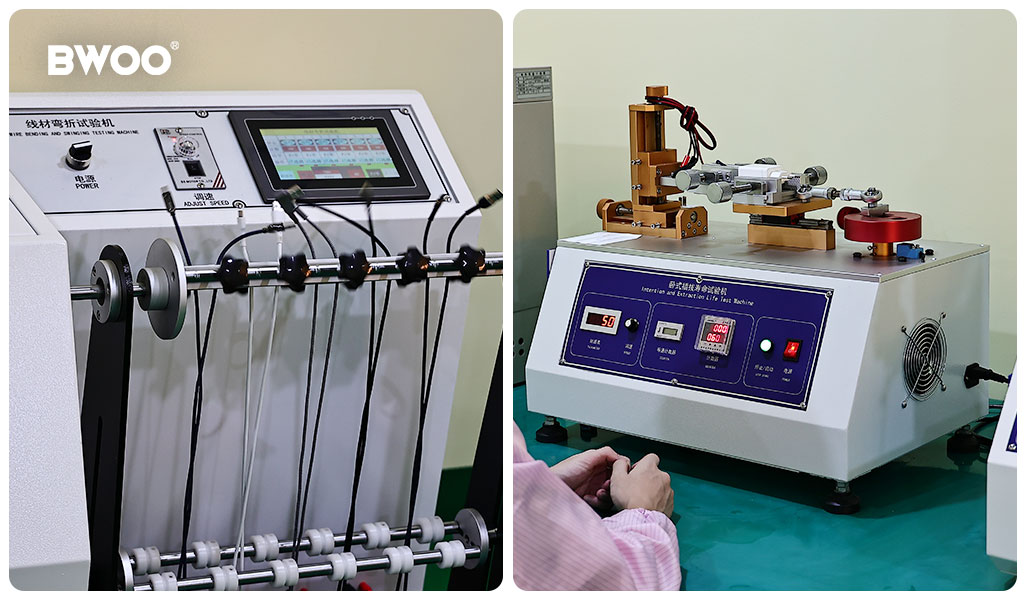
1. Bending Resilience Test
Industry benchmark:
According to widely adopted standards, the cable is fixed on a rotating arm and bent repeatedly at 60° or 90° angles.
What it simulates:
Daily stress at the strain relief (SR) area when users charge their devices while using them.
Typical data thresholds:
5,000 cycles: baseline qualification for mass-market products
10,000 cycles or more: industrial-grade durability
After testing, conductor resistance must remain within specified limits.
2. Constant Tensile Test
Industry benchmark:
The cable is subjected to a static load, typically 5–10 kg, for a defined duration.
What it evaluates:
Not just the outer jacket, but the internal reinforcement fibers and the solder joints between conductors and connectors.
Failure criteria:
Excessive elongation
Structural separation
Signal or power interruption
3. Mating Force & Life Cycle Test
Industry benchmark:
USB-IF specifications define up to 10,000 insertion and removal cycles for Type-C interfaces.
How it's tested:
Automated machines insert and remove the connector at a constant speed.
Key observation:
Post-test insertion and extraction force must remain within tolerance.
Too loose leads to unstable charging; too tight risks damaging device ports.
4. Salt Spray & Environmental Aging Test
Industry benchmark:
Exposure to a 5% salt mist environment for 24–48 hours, under controlled temperature and humidity.
Purpose:
To simulate high-humidity and coastal environments.
Acceptance requirements:
Connector surfaces must show no corrosion, oxidation, or coating degradation, and electrical conductivity must remain stable.
Structural Design Factors That Determine Cable Durability
Extended Strain Relief (SR) Design
Longer SR structures distribute bending stress over a wider area, reducing fatigue concentration at the connector joint.
Internal Shielding & Braiding
Aluminum foil layers not only reduce signal interference but also act as a secondary structural framework under repeated stress.
Outer Jacket Materials
TPE: high elasticity and flexibility
PVC: cost-effective with moderate durability
Braided nylon: superior abrasion resistance and tensile strength
Each material choice directly affects long-term mechanical performance.
Why Testing Standards Matter to Buyers
Lower failure rates:
Cables that meet industrial reliability standards are less prone to short circuits and internal breakage.
Global compatibility:
Compliance with CE, RoHS, and related mechanical reliability requirements is a basic threshold for international distribution.
BWOO's role:
With over two decades in the mobile accessories industry, BWOO consistently follows these widely accepted testing protocols, ensuring every production batch undergoes complete reliability validation before shipment.
Conclusion
Durability is an invisible cost.
A truly reliable data cable is not defined by how hard it is to break once, but by how well it maintains performance after years of repeated, real-world use.
Comment
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required. Required fields are marked*












































Comment
There are no comments yet!