The 5mm Rule of Magnetic Wireless Charging Explained

2026-02-03 16:30

Many users buy magnetic wireless power banks expecting convenience, only to find charging speeds surprisingly slow.
Then comes the moment of discovery: remove the phone case, and charging suddenly improves.
Why can a thin phone case make such a dramatic difference?
The answer lies in a widely accepted industry principle known as the "5mm rule"—a physical limitation that defines the real efficiency boundary of magnetic wireless charging.
What Is the "5mm Rule" in Magnetic Wireless Charging?
Definition:
Most Qi-based and magnetic wireless charging systems are designed to operate within an effective transmission distance of 0–5mm.
Underlying physics:
Wireless charging transfers energy through an electromagnetic field generated between a transmitting coil and a receiving coil.
Energy loss behavior:
Magnetic field strength decreases exponentially as distance increases.
In real-world conditions, each additional 1mm can reduce charging efficiency by 10–20%.
The critical threshold:
Once the total distance (case thickness + air gap + alignment loss) exceeds 5mm, energy transfer drops sharply.
This often results in unstable handshakes, extremely low current, or charging failure altogether.
How Phone Cases Quietly Drain Charging Efficiency
1. Physical Separation: Distance Is Resistance
The thick-case trap:
Many rugged or shockproof cases measure 3–4mm thick.
When combined with magnetic modules and unavoidable air gaps, the system quickly approaches the 5mm limit.
The result:
The charger attempts to compensate by outputting more power, but most of that extra energy is lost as heat rather than stored in the battery.
2. Magnetic Misalignment: When Coils Don’t Line Up
If a case is thick and lacks a built-in magnetic ring, magnetic attraction weakens, increasing the risk of coil misalignment.
Misalignment equals inefficiency:
Even a few millimeters of offset can cause the receiving coil to capture only a fraction of the magnetic field, cutting efficiency dramatically.
3. Heat Accumulation: The Hidden Battery Killer
Phone cases not only increase distance—they also trap heat.
When heat cannot dissipate, devices activate thermal protection mechanisms, intentionally slowing charging to protect battery health.
How BWOO Optimizes Charging Within the 5mm Limit
Rather than fighting physics, BWOO focuses on design optimization that works within the 5mm rule.
Ultra-Thin Magnetic Ring Design
BWOO magnetic accessories, including power banks and phone cases, use high-permeability N52 magnetic cores, delivering strong alignment while maintaining a slim profile.
Intelligent Foreign Object Detection (FOD)
Advanced control chips accurately detect interference beyond the optimal range and reduce output or alert users, preventing unnecessary heat buildup.
Optimized Coil Winding Structure
Compared with common factory designs, BWOO employs higher-density copper coil windings, improving magnetic field penetration and maintaining up to 90% conversion efficiency, even with compatible cases attached.
Buying Advice for Consumers and B2B Buyers
Check thickness: For wireless charging, choose phone cases under 3mm whenever possible.
Check materials: Avoid cases with metal plates, magnetic card holders, or ring stands unless specifically designed for magnetic charging.
Look for alignment support: Cases with integrated magnetic rings help pull chargers into optimal alignment, offsetting thickness-related losses.
Recommended Accessory for Optimized Charging
To stay within the 5mm efficiency window, BWOO recommends slim magnetic cases designed specifically for wireless charging.
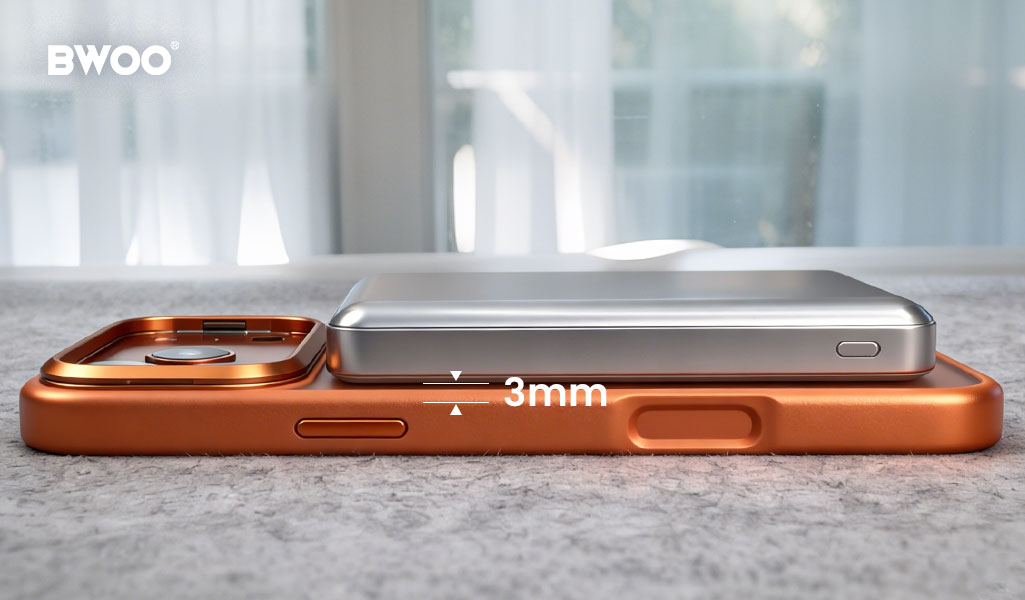
BWOO Matte Magnetic Phone Case for iPhone 17 (Model: BO-KI17M704)
Matte anti-fingerprint texture
Ultra-slim 3mm thickness
Raised edges for added screen and camera protection
Strong N52 magnetic core
Shock-absorbing anti-fall structure
Conclusion
The 5mm rule is not a marketing concept—it is a physical law.
Choosing properly designed accessories is not about faster charging alone, but about protecting long-term battery health and ensuring stable, efficient energy transfer.